
lunes, 30 de junio de 2014
miércoles, 25 de junio de 2014
Rosetta observa cómo cobra vida un cometa
Rosetta observa cómo cobra vida un cometa
24 de junio de 2014: Una nave espacial de la Tierra está a punto de hacer algo que ninguna nave espacial ha hecho antes: orbitar un cometa y descender en su superficie.
En este preciso momento, la sonda Rosetta, de la Agencia Espacial Europea (European Space Agency o ESA, por su sigla en idioma inglés), está lanzándose hacia el cometa 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. La misión de la nave espacial es estudiar el cometa de cerca, a medida que se transforma y deja de ser una calma perlita de hielo y roca, congelada hasta solidificarse debido a que ha pasado años en el espacio profundo, para convertirse en una dínamo que el Sol calienta y del cual emanan chorros de gas y polvo hacia una cola que se desarrolla de manera impresionante.
Noticia de último momento: La metamorfosis ha comenzado.

En un nuevo video de ScienceCast se adelanta la misión de Rosetta al cometa 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko. Reproducir el video (en idioma inglés)
“El cometa 67P está cobrando vida”, dice Claudia Alexander, una científica del proyecto Rosetta E.E.U.U., en el Laboratorio de Propulsión a Chorro (Jet Propulsion Laboratory o JPL, por su sigla en idioma inglés). “Y está más activo que lo que esperaba”.
Lanzada en el año 2004, Rosetta ha pasado los últimos años en “hibernación”, mientras se encaminaba hacia el cometa a través del sistema solar. En enero de 2014, con su destino a la vista, Rosetta despertó y encendió sus cámaras. Al principio, el cometa parecía ser un agujerito sin dimensiones, inactivo, excepto por su tranquilo movimiento a través del espacio. Luego, el 4 de mayo, una brillante nube apareció alrededor del núcleo.
“Está comenzando a verse como un cometa real”, dice Holger Sierks, del Instituto Max Planck para la Investigación sobre el Sistema Solar (Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, en idioma inglés), en Alemania, donde se construyó la cámara científica OSIRIS, de Rosetta. “Es difícil de creer”, señala, “que, dentro de apenas pocos meses, Rosetta se encontrará ubicada dentro de las profundidades de esta nube de polvo y estará en camino hacia el origen de la actividad del cometa”.
Algunas naves espaciales de la NASA, de la ESA y de otras agencias espaciales ya han volado cerca de ciertos cometas. Un ejército completo de naves espaciales visitó el cometa Halley a mediados de la década de 1980, en lo que fue un suceso internacional que todavía se considera un punto de referencia en el ámbito de la investigación sobre los cometas. Entre otros ejemplos para destacar se incluye a la misión Stardust (Polvo de Estrellas, en idioma español), de la NASA, que voló a través de la cola del cometa Wild en el año 2004 y que dos años después trajo las muestras a la Tierra; y la nave espacial Deep Impact (Impacto Profundo, en idioma español), que en 2005 dejó caer un proyectil sobre el cometa 9P/Tempel, produciendo un hoyo en su núcleo que permitió a los investigadores observar el interior.
Los sobrevuelos brindan información, pero Rosetta hará mucho más que eso.
“Un sobrevuelo es apenas un tentador vistazo de un cometa en una etapa de su evolución”, destaca Alexander. “Rosetta es diferente. Orbitará 67P durante 17 meses. Veremos evolucionar a este cometa justo frente a nuestros ojos mientras lo acompañamos en su camino de ida y vuelta desde el Sol”.

Primer plano del cometa 67P/C-G, el 30 de abril de 2014. Crédito:ESA/ Rosetta/ MPS por el equipo de OSIRIS, MPS/ UPD / LAM/ IAA/ SSO/ INTA/ UPM/ DASP/ IDA
El momento más emocionante de la misión probablemente se produzca en noviembre, cuando un módulo de descenso construido en Europa baje desde la nave espacial y se pose sobre la superficie del cometa. El módulo de descenso se denomina “Philae” por una isla del Nilo, el sitio donde hay un obelisco que ayudó a descifrar (¡sí, adivinó!) la Piedra de Rosetta.
Como los cometas tienen escasa gravedad, el módulo de descenso se anclará con arpones. “Quizás sus patas se entierren en algo crujiente como el permafrost, o quizás lo hagan en algo sólido como una roca”, especula Alexander.
Una vez que esté sujeto, el módulo iniciará un estudio de primera mano, sin precedentes, del núcleo de un cometa, mientras Rosetta continuará monitorizando los desarrollos de los procesos desde arriba.
A pesar de que Rosetta es una misión europea, la NASA ha contribuido con algunos importantes instrumentos para la nave espacial, y los científicos estadounidenses están tan ansiosos como sus colegas europeos por el arribo de Rosetta. Las fotografías tomadas recientemente han ayudado a los controladores de la misión a localizar a 67P y a comenzar una serie de maniobras que lentamente alinearán a la nave espacial con el cometa justo a tiempo para un encuentro que tendrá lugar en agosto.
“Nuestro objetivo está adelante”, afirma Alexander, “¡y Rosetta lo está alcanzando!”
| Créditos y Contactos | |
| Funcionaria Responsable de NASA: Ruth Netting Editor de Producción: Dr. Tony Phillips | Traducción al Español: Angela Atadía de Borghetti Editora en Español: Angela Atadía de Borghetti Formato: Angela Atadía de Borghetti |
National Aeronautics and Space AdministrationFuncionaria responsable de la NASA: Ruth Netting
Editor de Producción: Dr. Tony Phillips
¡Envíenos sus comentarios!
Última actualización: 25 de junio de 2014
Editor de Producción: Dr. Tony Phillips
¡Envíenos sus comentarios!
Última actualización: 25 de junio de 2014
viernes, 13 de junio de 2014
Haiti’s Gold Rush: An Ecological Crime in the Making
Haiti’s Gold Rush: An Ecological Crime in the Making

By Dady Chery
NEWS JUNKIE POST
Nov 29, 2012 at 7:21 pm
Show me a corporate boss who calls Haiti the “poorest country in the western hemisphere,” and I’ll show you a con artist preparing to fleece Haiti. Likewise, show me a western technocrat who bemoans Haiti’s “dramatic deforestation due to charcoal production” and I’ll show a bio-pirate or vandal preparing to wreck the country’s remaining cloud-forest and mangrove-forest ecosystems.
It turns out that the real plan for Haiti’s northeastern region — especially the Caracol Bay area — is one that was hatched by U.S. and Canadian mining corporations, with the U.S. and South Korean sweatshop zone being a side project and distraction. If this mining plan is given a green light while Haiti is under foreign occupation, it will permanently strip the country of much of its mineral, cultural, and ecological wealth.
In a May 1, 2012 interview with Canada’s Financial Post, Majescor Resources Inc. CEO Dan Hachey was effusive about Michel Martelly’s installment as president because he expects Martelly’s policy of mimicking the Dominican Republic (DR) to be a boon to the mining sector. Hachey enthusiastically noted that “thirty years ago, there was no mining sector to speak of in the Dominican Republic…. In that short period of time they’ve seen the development of the Pueblo Viejo Project [of Barrick and Goldcorp's], which is one of the world’s largest gold deposits — and is pretty much a neighbour of ours…. They’re going to be coming on with production this year.”
This glowing picture omits the fact that Barrick and Goldcorp have come under strong popular opposition in the DR. In a country where 20 percent of the population lacks access to drinking water, these companies are accused of polluting 2,500 cubic meters of water per hour with the vast quantities of cyanide needed to process 24,000 tons of ore a day by opencast (or open-pit) mining. Open-pit mining is banned by the European Union. Activists in the DR have joined forces with a broader group called Observatorio de Conflictos Mineros de América Latina (OCMAL) that launched a campaign to end this practice in the region. These problems are compounded by the damages from the more intense tropical storms due to climate change. For example, in the Philippines, the largest gold mine had to be suspended due to an unexpected spillage of waste into a major river. In the DR, there is great concern that the country’s biggest water reservoir, which is close to the mining operations, is continuously at risk of cyanide contamination, since stories of spills and massive fish die offs caused by mining companies are legion. Barrick and Goldcorp have also been accused of dynamiting mountains and destroying Taino Indian archaelogical sites.
Like the Pueblo Viejo region of the DR currently under exploitation, the spot being eyed for mining by Majescor in Haiti — a 50-square-kilometer area called the SOMINE property — belongs to a broader region, replete with archeological sites, situated along a metal-rich mountain ridge running from southeastern DR to northern Haiti. This was formerly known simply as Le Massif du Nord but has become the “Massif du Nord Metallogenic (or Mineralization) Belt.”
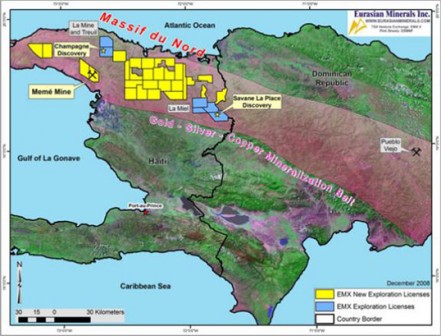
An EMX-Newmont joint venture and the Haitian government signed a Memorandum of Understanding in April 2012 that allows exploration drilling while a Mining Convention is being ratified to permit development. Under this MOU, a gold prospect called Savane La Place is the first project picked for drilling.
SOMINE is an acronym for Société Minière du Nord-Est S.A. and is described in the mineral trade sheets as a “Haitian affiliate mining company.” It is 66.4 percent owned by Majescor, with the rest being owned by unidentified members of Haiti’s elite. Majescor is still a relatively small company that conducts mineral surveys. The SOMINE property is surrounded by other mining properties owned jointly by Majescor and much larger concerns likeEurasian Minerals and Newmont Mining. Once Majescor’s surveys are complete, it plans to find a big partner, like Eurasian, Newmont or Barrick (or some partnership of these like EMX-Newmont), to handle the extractive part of the project.
Curiously, the area of the SOMINE property was initially surveyed as early as “the 1970s by the UN Development Program, with some very good results [but the project was not pursued. Then] there was a feasibility study done by the Germans [Bundesanstalt fur Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe (BGR)] in 1980, and there was further drilling done in the 1990s by Canadian junior [mining companies],” recalled Hachey. During the 1980′s, the area was explored again by the UNDP and also surveyed by the French Bureau de Recherches Géologiques et Minière (BRGM), both of which reported finding only copper. The official story is that an abundance of copper had until 2012 obscured the fact that the area’s ore is also rich in silver and gold, and this was discovered from Majescor’s recent prospects of Douvray, Blondin and Faille-B. However, the story could just as well be that the mining executives were biding their time and waiting for a “stable” non-nationalistic government to take effect before initiating their projects.
Indeed, the issue of gold mining could have been one of the undeclared motivations behind the February 2004 removal of Aristide. The post-coup government immediately went to work signing away Haiti’s mineral rights without any knowledge of the public. For example, the mineral rights to the SOMINE property were quietly assigned under a Mining Convention executed between this company and the coup government on May 5, 2005 and presumably valid until March 9, 2020. In any case, after the coup, Haiti’s mountains suddenly began to glitter. For example, an exploration of the Faille-B prospect in 2007 reported a gold vein that averaged 42.7 grams of gold per ton of ore (g/t) over 6 meters, including values of 107.5 g/t of gold over one meter.
According to Hachey, April 11, 2012 assays from Blondin found:
- 0.45 percent copper over 96.5 meters;
- 0.3 percent copper over 12 meters, including 0.61 percent copper over 1.5 meters; 154 grams of silver per ton (g/t) over 12 meters, including 869 g/t silver over 1.5 meters.
March 13, 2012 results from Blondin discovered:
- 72.4 g/t silver over 15 meters;
- 16.9 g/t silver over 113 meters, including 6.2 g/t silver over 1.5 meters; 0.43 percent copper over 113 meters, including 4.44 percent copper over 1.5 meters.
February 1, 2012 results from Douvray discovered:
- 255 g/t silver over 13.5 meters, including 2,069 g/t silver over 1.5 meters; 0.35 percent copper over 13.5 meters, including 0.52 percent copper over 1.5 meters; 0.02 g/t gold over 13.5 meters, including 0.04 g/t gold over 1.5 meters;
- 277 g/t silver over 13.5 meters, including 1,428 g/t silver over 1.5 meters; 0.18 percent copper over 13.5 meters, including 0.52 percent copper over 1.5 meters; 0.04 g/t gold over 13.5 meters, including 0.04 g/t gold over 1.5 meters.
These highly concentrated deposits of copper, silver and gold should reasonably represent a new found wealth for Haiti during a dire need of resources for the country’s reconstruction. But if the DR is to serve as an example, Haiti will not benefit from its minerals. In the DR, Barrick owns 60 percent of the Pueblo Viejo gold mine and Goldcorp Inc. owns the remaining 40 percent. To get a sense of the scale of the greed, one need only consider that, while gold currently costs over $1,700 per ounce, the Pueblo Viejo mine is slated to produce one million ounces of gold per year at a cost of only $20-50 per ounce, making it one of the lowest-cost gold mines in the world.
Hachey comments with evident enthusiasm: “What we’re most excited about is that we found some silver which was never really realized before. It’s the first silver discovery in Haiti…. Part of the reason why it was never really discovered was that historically there was so much copper prevalent — there’s a lot of outcropping at the surface. The people who did the work before did not do much testing, even for gold…. The geology is a little complex for a copper porphyry, but in a good way. The surprises that we’re getting are all good ones.”
As major draws for a big mining partner to this next phase of the project, Hachey is advertising that, unlike Port-au-Prince, which was destroyed by the earthquake, Cap Haitien is a pleasant place for a Canadian mining executive and his family to come to. In addition, he notes that there are plans for “the construction of a deep-water port at Caracol,” only 15 kilometres from the SOMINE property and near Cap-Haitien. Indeed, on May 7 Martellyannounced that the construction of a port would soon start in Fort-Liberte (near Caracol), in the Northeast. The port will cost $179 million and is supposed to be “built with the U.S. government’s help,” but it will likely be entirely owned by U.S. concerns. This first official announcement of a deep-water port for Caracol explains in part why there has been no effort to mitigate the ecological effects of the massive free-trade (sweatshop) zone inaugurated in October 2012 in that area: the textile factories’ contributions to the degradation of Caracol Bay should be trivial compared to the damage from opencast gold mining and construction of a deep-water port.
UPDATES on December 21 and 28, 2012, Associated Press, VCS Mining. Under cover of the holidays, Haiti’s Mining Director Ludner Remarais issued a gold exploitation permit to VCS Mining LLC (and its wholly-owned subsidiary Delta Societe Miniere S.A.), a U.S. company based in North Carolina, and gold and copper exploitation permits to SOMINE S.A. SOMINE is 66.4 percent owned by Canada’s Majescor Resources Inc and 33.6 percent owned by a group of unidentified, and possibly nonexistent, Haitian investors. According to Majescor CEO Dan Hachey: the permit “allows us to finally produce and make money, at least get to that step…. It’s also a great step forward for the mining industry in Haiti.” SOMINE engineer Michel Lamarre said he expects exploration to start in 36 to 42 months, and VCS CEO Angelo Viard expects his company to enter into “production” within 29 to 38 months. The gold permits are for five years and renewable for up to 25 years, with a possible renewal for another 10 years if new resources are discovered. These permits were issued by Remarais without any environmental-impact assessment (EIA).
UPDATE on January 24, 2013, Defend Haiti. After a meeting of Haiti’s Senate Committee on Public Works and Communication, Minister of Public Works, Transportation and Communication Jacques Rousseau, and Director General of Mining and Energy Ludner Remarais on Tuesday January 22, 2013, the Senate met and rejected the agreements made by Remarais with the U.S. and Canadian mining companies in December 2012, pending a review of the companies and the agreements.
UPDATE on April 10, 2014, Miami Herald. Plans to dig a deep-sea port in Fort-Liberte, near Haiti’s Caracol Bay area, have been scrapped. If the plans had gone ahead, they would have destroyed a rare hotspot of biodiversity in the Caribbean with Haiti’s largest remaining mangroves and such a breathtaking variety of corals that the area had been slated to become a World Heritage Site and marine park. Apparently the controversy around the project discouraged potential investors. Instead of destroying Fort Liberte Bay, the existing port in Cap Haitien will be expanded, although its current operations are ten-fold under capacity.
Editor’s Note: News Junkie Post co-Editor in Chief, Dady Chery, broke this story on May 2, 2012. Photograph one by Sky Truth; photographs two, five and six by United Nations Photo. Photograph four by Stormy Dog and photograph seven by Andrew Kuznetsov. Photographs eight, nine and ten by Alex Proimos.
Related Articles
- January 11, 2013 Haiti: Where Demolition and Exploitation Pass for Reconstruction and Development
- December 2, 2013 Dominican-Haitian Tensions: Wag the Dog or Prelude to Genocide?
- January 11, 2014 On Haiti’s Earthquake Anniversary: Still Waiting for Godot
- April 21, 2014 What Kind of Tourism Is Sustainable for Haiti’s Ile a Vache? Interview With Melinda Wilson
- October 23, 2013 Haiti: Where Democracy and Justice Make a Stand Against Corrupt Power
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)


















































8 Responses to Haiti’s Gold Rush: An Ecological Crime in the Making